
With its amazing performance and flexibility, KVM has become the most popular choice for virtual private servers (VPS) in recent years. But what makes KVM VPS stand out from other virtualization technologies?
In this blog, we’ll explain what is a KVM VPS, dive into its pros, and cons and explore why it has become the most popular VPS solution for businesses of all sizes.
A Virtual Private Server (VPS) is a type of web hosting service that offers a middle ground between shared hosting and dedicated hosting. In a VPS setup, a single physical server is divided into multiple virtual servers using virtualization technology. Each virtual server operates independently with its own dedicated resources, including CPU, RAM, disk space, and operating system. Some of the popular virtualization technologies are OpenVZ, XEN, KVM, Hyper-V, VMware ESXi, etc.
What is KVM VPS?
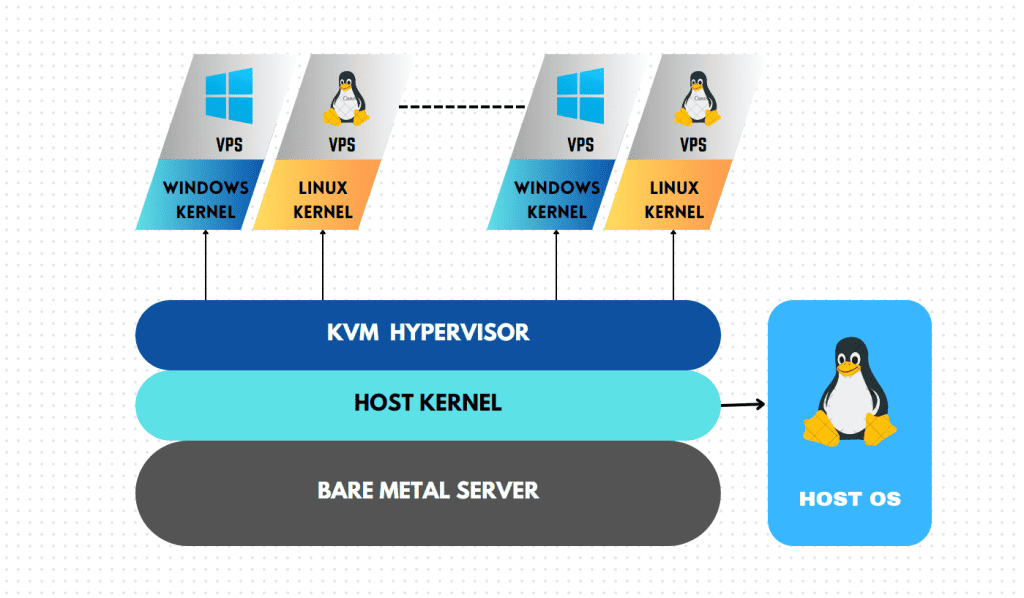
KVM (Kernel-based virtual machine) is an open-source virtualization technology to set up VPS. A virtual machine (VM) functions as a virtual independent computer system and it is built on a single hardware system. And hypervisor is the software layer used to create and manage these VMs.
KVM allows the creation and management of VMs on a Linux-based host system. The host system runs the Linux kernel with the KVM module, which acts as the hypervisor and is responsible for implementing the core virtualization capabilities within the Linux kernel. The KVM module leverages the hardware virtualization extensions provided by modern processors (such as Intel VT-x or AMD-V) to create and manage VMs.
The name “Kernel-based Virtual Machine” reflects the key aspects of the KVM server technology. KVM is integrated into the Linux kernel as a kernel module and it enables the creation of VMs, thus it is aptly named “Kernel-based Virtual Machine”.
The Advantages of KVM VPS
1. Performance
KVM offers excellent performance due to its efficient integration with the Linux kernel and hardware virtualization extensions. It allows direct access to host hardware resources, resulting in low latency and high throughput for virtual machines. KVM’s performance is comparable to running applications natively on the host machine.
2. Full Virtualization
KVM provides full virtualization capabilities, allowing you to run multiple virtual machines (VMs) with different operating systems on a single host. Each VM runs its own independent kernel, enabling you to use a wide range of operating systems, including Linux, Windows, BSD, and others.
3. Scalability
KVM is an established virtualization solution with a stable codebase and long history of development. It benefits from being a part of the Linux kernel, which provides continuous updates, security patches, and widespread hardware compatibility. It is widely adopted and trusted by many organizations and enterprises.
4. Resource Efficiency
KVM enables efficient resource allocation and utilization. It provides granular control over resource allocation, allowing administrators to allocate CPU cores, memory, storage, and network bandwidth to VMs as needed. KVM also supports overcommitting resources, where the total allocated resources can exceed the physical capacity, leveraging the assumption of not all VMs use their allocated resources fully at the same time.
5. Security and Isolation
KVM provides enhanced security through isolation between virtual machines. Each VM runs its kernel and operates in its isolated environment, which helps prevent one VM from affecting others. Additionally, KVM benefits from the security features provided by the underlying Linux kernel, such as SELinux and mandatory access controls.
6. Open-Source and Ecosystem Support
KVM is an open-source technology with the support of a large community of developers and contributors. This active community ensures continuous improvement, bug fixes, and the availability of various tools and resources to support KVM deployment and management. It also enjoys support from major industry players, such as Red Hat, which provides commercial solutions and ecosystem support around KVM.
7. Cloud Compatibility
KVM is made use of by cloud platforms and infrastructure providers, including OpenStack. Its compatibility with cloud environments allows for seamless deployment and management of virtual machines in cloud infrastructures.
The Disadvantages of KVM VPS
1. Complexity
KVM, being a kernel-level virtualization technology, may require a deeper understanding of the underlying system and Linux administration compared to user-level virtualization solutions. Configuration and management of KVM may involve working with command-line tools and interacting with the Linux kernel, which can be more complex for users who are less familiar with these aspects.
2. Steeper Learning Curve
KVM may have a steeper learning curve for users who are new to virtualization or have limited experience with Linux. Understanding virtualisation concepts, working with hypervisor configurations, and managing VMs in a command-line environment can take time and effort to grasp effectively.
3. Hardware Requirements
KVM relies on hardware virtualization extensions (such as Intel VT-x or AMD-V) available in modern processors. While most recent processors support these extensions, older hardware or certain low-power devices might not have the necessary capabilities. This limitation can restrict the use of KVM on specific hardware platforms.
4. Host System Dependency
KVM is closely tied to the Linux kernel, meaning that it primarily runs on Linux-based host systems. While there are efforts to port KVM to other operating systems, its native and most mature implementation remains on Linux. This limitation can be a disadvantage if you require virtualization on non-Linux platforms.
5. Management Tools
Although KVM provides a solid foundation for virtualization, the ecosystem around management tools and graphical user interfaces (GUIs) may vary in terms of maturity and features compared to more established virtualization platforms. While there are management solutions available (such as virt-manager and web-based interfaces), their capabilities and ease of use may not be as extensive or polished as those offered by commercial hypervisors.
6. Limited Live Migration Support
KVM’s live migration feature allows moving running VMs from one host to another without service interruption. However, live migration support may have some limitations depending on the specific configuration and underlying infrastructure. Live migration might not be possible between different processor architectures or in certain network environments, which can impact workload mobility.
It’s important to note that these disadvantages are not universal and may be mitigated by expertise, hardware compatibility, available management tools, and specific use cases. Organizations or individuals evaluating KVM should carefully consider their requirements, available resources, and technical proficiency to determine if KVM is the right choice for their virtualization needs.
KVM Virtualization Vs Others
KVM is a type 1 hypervisor that provides full virtualization, which means that each VM runs its own kernel and has direct access to the underlying hardware resources. This direct access to hardware resources allows KVM to provide near-native performance and strong isolation between VMs, enhancing security. Its use of hardware-assisted virtualization also provides a strong security foundation.
1. KVM Vs Container-Based Virtualization
In contrast, container-based virtualization, such as Docker, provides a lightweight virtualization solution that shares the host kernel and resources among multiple containers. Containers are isolated at the application level rather than at the kernel level, which means that they can share the same kernel and libraries, reducing the overhead and increasing efficiency. Container-based virtualization is ideal for lightweight applications that require fast deployment and efficient resource utilization.
However, container-based virtualization may introduce some security risks as all containers share the same kernel and libraries. Malicious activity in one container may affect other containers and the host. Additionally, containers may not provide the same level of isolation and performance as KVM.
2. KVM Vs Type-2 Hypervisor
Another virtualization technology is Type 2 hypervisors, such as Oracle VirtualBox and VMware Workstation. Type 2 hypervisors run on top of the host operating system and provide virtualization services to guest operating systems. Type 2 hypervisors provide good isolation between VMs and compatibility with various operating systems. However, they may introduce some overhead due to running on top of the host operating system and sharing its resources.
Type 2 hypervisors are ideal for development and testing environments or running multiple operating systems on a single machine. However, they may not provide the same level of performance and security as KVM.
Why is KVM VPS the most preferred?
KVM is currently the most popular choice for virtualization due to its excellent performance, strong security, flexibility, management capabilities, and cost-effectiveness. KVM’s use of hardware-assisted virtualization, implementation as a type 1 hypervisor, and direct access to hardware resources provide near-native performance and strong isolation between VMs. KVM also provides great flexibility in terms of resource allocation, compatibility with various operating systems, and advanced features like device passthrough.
While other virtualization technologies like container-based virtualization and Type 2 hypervisors have their advantages, they may not provide the same level of performance and security as KVM. Container-based virtualization is ideal for lightweight applications, while Type 2 hypervisors are ideal for development and testing environments. However, for resource-intensive applications, KVM is the preferred choice due to its superior performance and security.
Is KVM Available Windows?
While KVM was originally developed for Linux, it has been ported to other operating systems, including Windows and FreeBSD. For example, the OpenStack cloud computing platform supports KVM on multiple operating systems, including Linux, Windows, and FreeBSD. This enables users to run virtual machines on KVM regardless of the operating system.
In addition, KVM can be used with various management tools that support multiple operating systems, such as oVirt and Virt-manager. These tools provide a user-friendly interface for managing KVM virtual machines on different operating systems.
Moreover, KVM is supported by several cloud service providers, including Amazon Web Services, Google Cloud Platform, and Microsoft Azure. These cloud providers offer KVM-based virtual machines as a service, allowing users to run their applications on KVM without having to worry about managing the underlying infrastructure.
In summary, while KVM was originally developed for Linux, it has been ported to other operating systems, and various management tools and cloud providers support KVM on multiple operating systems. Therefore, it is not accurate to say that KVM is only available on Linux.
Is KVM VPS the Right Fit For You?
Deciding whether a KVM VPS is the right fit for your needs can be a complex decision that depends on a variety of factors, such as your budget, technical expertise, and specific requirements for your applications or website.
Consider the below requirements and find out whether KVM VPS is the right choice for you or not;
- Resource Requirements: Applications or websites that require significant computing resources, such as CPU, RAM, and disk space, will have success with using KVM. It’s important to assess your resource needs and make sure that the VPS plan you choose can provide enough resources to meet those needs.
- Technical Expertise: This virtualization requires some technical expertise to set up and manage. If you’re not comfortable with command line interfaces, server administration, and troubleshooting, you may want to consider a managed VPS service instead.
- Scalability: If your applications or websites experience fluctuations in traffic or resource usage and requires scaling up and down as per the need of the hour, then KVM is an excellent choice for you. Make sure to choose a VPS provider that offers easy scalability options.
- Budget: It can be more expensive than other types of VPS due to its high-performance capabilities. Make sure to evaluate your budget and consider whether the added performance and features are worth the additional cost.
- Operating System Support: KVM supports multiple operating systems, including Linux and Windows. Make sure to choose a VPS provider that offers the operating system you need for your applications or website.
What to look for in a KVM VPS provider?
Once you have evaluated these factors, the next step is to evaluate VPS providers and then you will be able to make an informed decision
- Research VPS providers that offer KVM virtualization technology and compare their plans and pricing to determine which provider offers the best fit for your needs.
- Read reviews and ratings from other customers to gauge the provider’s reputation for reliability, support, and performance.
- Contact the provider’s customer support team and ask any questions you may have about their KVM VPS plans and features.
- Try a KVM VPS plan for a short period of time. Test its performance and determine if it meets your needs before committing to a long-term plan.
In a Nutshell…
KVM server technology offers a wealth of benefits that make it a top choice for businesses in need of high-performance virtual private servers.
KVM stands out as a powerful solution that can help you take your business to the next level. However, like any technology, KVM does come with its own set of drawbacks. And it’s important to weigh these against the advantages before making a decision. By understanding the benefits and limitations of KVM, you can make an informed choice that meets your specific hosting needs.
So, what are you waiting for? Try out Veeble KVM VPS today and see why it has become the gold standard in server virtualization!
