
We live in a world that is becoming more and more data-driven with each passing day!
This has made our life easy and fast-paced. However, we cannot turn a blind eye to the consequences of this digital transformation even if we want to.
Data breaches and cyber-attacks are getting worse and it has already reached an enormous magnitude. There are various kinds of cyber attacks, but phishing is one of the most common forms of internet crime.
Phishers steal money and data from internet users. Any business or individual needs to keep their information secure. A phishing attack can be deadly for businesses, so taking preventive measures and necessary precautions is always the better alternative.
So, let’s try to understand phishing attacks in detail!
What is Phishing?
Phishing, also known as brand spoofing or carding is an ongoing cyber security threat that is being faced by millions of people on the internet. It is estimated that around 156 million phishing emails are sent every day to email users and possibly around 80000 are likely to click on them.
The main purpose of this attack is to steal money and data of the internet users like credit card information, passwords, date of birth, social security numbers, and other sensitive information online.
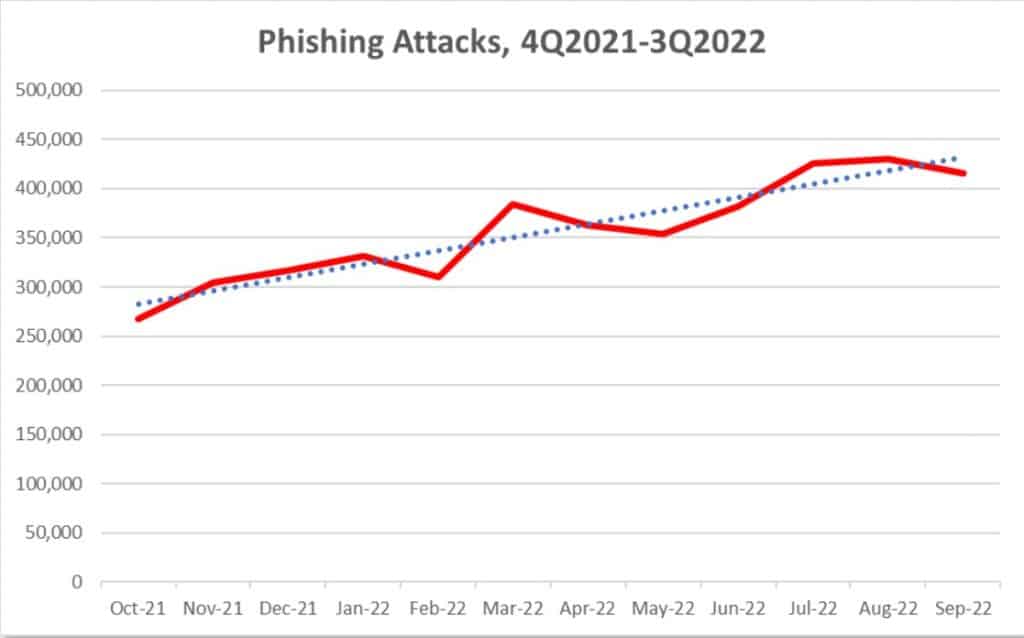
APWG Phishing Activity Trends Report
- In the third quarter of 2022, APWG observed 1,270,883 total phishing attacks, a new record and the worst quarter for phishing that APWG has ever observed.
- Fewer companies were victimized by ransomware than at any point since early 2021.
- Attacks against the financial sector represented 23.2% of all phishing attacks.
- Business Email Compromise (BEC) attacks continued to be troublesome, and the number of wire transfer BEC attacks in Q3 increased by 59%.
- Advance fee fraud scams launched via email increased by 1,000% in Q3.
We are going to discuss various types of phishing attacks and countermeasures you can take which will help you deal better if you ever encounter such an attack.
9 Common Types of Phishing & Their Effective Preventive Strategies
1. CEO Fraud
CEO Fraud or Business Email Compromise Attacks has caused losses in the billions of dollars, at large and small companies!
In this method, the email is sent to a junior employee of the company pretending to be the CEO of the company to carry out some tasks. The phisher will usually ask the victim to send a specific amount to a fake account.
The attacker uses two ways to carry out this attack in the first method, they spoof the CEO’s name, but the email address will be different in the second method they mimic both the CEO’s name and the email address which will make the victim harder to identify the source.
How to prevent or mitigate CEO fraud?
- Check whether the source email is from an authentic user or not
- Verify the email is signed using a certificate
- Quickly check the style of writing and spelling
- Train the employees to help them gain proper security awareness
- Configure the email server with proper settings to block such spoofed emails
- Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting & Conformance (DMARC) should be employed to prevent domain spoofing to block the domain which is sent from a spoofed email address
These are some of the precautions you can take to ensure your organization won’t become a victim of CEO fraud.
2. Spear Phishing
Spear phishing is used by attackers to steal sensitive information from targeted individuals, businesses, and organizations. The attackers use a specific approach for each person with proper social engineering to ensure the victims fall into their trap. They send a phishing email to the user as a friend of the victim or a reliable person.
Consequently, the victims click on the malicious link and visit a fraudulent website that looks so genuine and convincing to the victim.
As a result, malware is downloaded to the victim’s computer which allows the attackers to gain access to the sensitive information stored on the computer.
Also, the victims’ email accounts will be compromised by the malware which enables attackers to gain access to these email accounts and thus they can send emails under the victim’s authority.
Most of these attacks are done by hacktivists and government-sponsored hackers. The government and private companies buy confidential data from these cyber criminals so they can take advantage of their competition and their enemies.
Ways to ensure protection from Spear phishing
- Implement anti-phishing software along with anti-spam and antivirus filters
- Use digital risk protection platforms like PhishLabs, IronScales, and PhishMe
- Keep your system up-to-date with the latest security
- Keep all the sensitive information encrypted
Spear phishing employee training
- Read the URL completely and ensure its genuine
- Don’t fall for ‘double-barrelled phish’. In this, the victim often messages the spoof email to check whether it is the person they know. The phishers are now clever and reply that they are the very same person but only after a delay, which makes it more believable.
- Don’t open a PDF file from an unknown email. It could contain malicious zip files.
- Don’t provide your password or other personal/sensitive information to an unsolicited email.
3. Vishing
Vishing, also known as voice phishing, is a phishing activity that is carried out over voice during a phone call. The attackers who call will impersonate themselves as a person from an official bank or law enforcement and ask you to provide certain information which they can use to steal the money and your identity.
Vishing (voice phishing) cases increased by almost 550% from Q1 2021 to Q1 2022.
Quarterly Threat Trends & Intelligence Report from Agari and PhishLabs
The attackers can approach their victims by using email, phone calls, text messages, or social media chatting. The victims think that they are coming from a trusted source and they will be forced to give out their sensitive information. This is because scammers use voice-over-internet protocol (VoIP) to spoof their caller identification to make the phone call look trustable to their victims.
Vishing Prevention: Things to Keep in Mind
- Don’t give multi-factor authentication details, passwords, financial data, or similar details over the phone under any circumstances.
- Always make sure the phone calls are legitimate by taking the name of the caller and cross-checking it with the organization they mentioned.
- Keep in mind the fact that no organization will make you pay via prepaid credit or gift card.
- Never give remote computer access to anyone except your IT department
- Train your employees to notice and report any suspicious activities.
4. Smishing
This cyber-attack is carried out by sending SMS to mobile devices with false information which tricks victims to submit their sensitive information to a malicious website.
For example, here the attackers create false offers for any e-commerce websites with huge discounts and make the victims enter their important credit card information on the malicious website which will cost a huge loss of money.
The attackers will use social engineering to study their targets to send clever messages which creates panic in victims and thus they would blindly follow the instructions given in the text message. Also, more people are inclined to fall for SMS scams compared to email scams because the SMS cannot be easily ignored after it is received on the user’s mobile device.
Smishing attacks are often carried out using shortened links. Shortened links are short versions of the actual link, which reduces the text in the link and thus hides the domain behind the link. Only after clicking the link, the users will be able to see the full link. In the meantime, the scammers will have already begun a malware attack.
The smishing attackers also use the option of saying that if you do not click a link and enter your personal information, you will be charged per day for using a service. The user should ignore the message if they signed up for the service. The user should make a complaint to their bank if they notice any unauthorized charges on their credit card or debit card statement. The bank will always support the victim and they would rectify the problem if it is possible.
How to Mitigate Smishing Attacks
- The best way to ensure you are protected from smishing attacks is by not opening suspicious SMS. Urgent!!, Hurry Up!!, etc are some of the most common wordings found in smishing SMSs. Make sure you don’t click any links or download anything from such a message before ensuring its credibility.
- Don’t keep critical and financial information in a text file on your mobile devices.
- Ignore spam messages and messages that contain shortened links.
- Report all smishing attempts to authorities
- Download an anti-malware app that can protect your mobile device against smishing text messages.
5. Ransomware Attack
Each organization must address ransomware, which is a form of malware that is designed to extort money from victims; and phishing, which is the preferred delivery mechanism for ransomware and other malware. Phishing spam attachments, which arrive in the victim’s email inbox masquerading as a file they should trust, are one of the most common delivery systems.
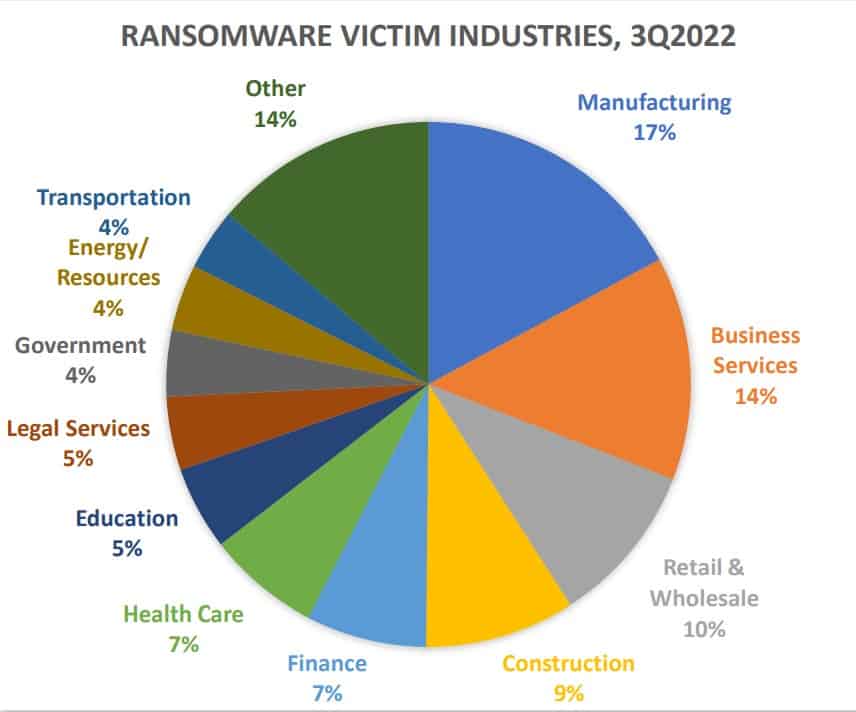
These attacks can take over the victim’s computer once the ransomware has been opened and downloaded, especially if they have built-in social engineering tools that trick users into granting administrative access. Some files are programmed to find any vulnerability in the user system and gain access automatically.
Once the malware has taken over the system it will encrypt files on the system with a different format that cannot be opened by the user. Once the user tries to access the files, the malware will warn the user that their files are encrypted and they would be asked to pay a certain amount to an anonymous account or a cryptocurrency wallet once it is done, the malware may or may not unencrypt the file. So, it is not guaranteed that even if the user pays the money, it will be accessible to them.
Top-level organizations, hospitals, and universities are most targeted by the ransomware attack because the attackers could encrypt critical data that is very important to the organization and ask for a good amount of money as ransom. Even though these are the main victims, the ransomware tends to spread automatically, and anyone can become a victim based on their actions and their system security.
Helpful Tips to Deal with Ransomware Attacks
- Backing up data daily, thus your organization won’t be forced to pay ransom for encrypted data.
- Keep your operating system and software always updated
- Install antivirus software and firewalls
- By using network segmentation, an organization can divide its network into smaller networks and isolate ransomware.
- By whitelisting applications, unauthorized programs and websites that are not whitelisted will be restricted or blocked in the event a user or employee accidentally downloads an infected program.
6. Snowshoe Spam Attack
This is another form of attack that is used to spread spam emails to perform phishing activity. The first cases of snowshoe spam email were discovered in 2009, but it was not until 2014 that this gained traction. This is a spamming tactic in which the spammer distributes his spam through many IP addresses and domains. This enables spammers to sometimes fool and evade spam filters, allowing some of their unsolicited emails to hit users’ inboxes.
To understand the terminology better, we will look at what exactly is a snowshoe. The purpose of snowshoes is to distribute weight over a wide area so that the wearer will not succumb to ice and snow crusts. Similarly, snowshoe spamming distribute spam across a wide range of IP addresses in much the same way.
Snowshoe spam often masquerades as a legitimate bulk email. The bulk email was still a valid and widely used email marketing tactic in 2009. For the most part, that is no longer the case, and even perfectly legal bulk emails will result in your email being marked as spam. Snowshoe spammers use a variety of fictitious company names, including “doing business as” (DBA) and “false identities,” and they change voicemail and postal drop boxes daily.
The domains purchased and used by the Snowshoe spammers are protected by their domain registrars using the privacy protection feature. So, hunting down the domain owner and submitting an abuse complaint is nearly impossible. Spammers, spyware, and other harmful practices are impossible to track down in countries with anti-spam laws, mostly because criminals know how to hide their tracks.
Ways to Ensure Protection Against Snowshoe Spam Attacks
- Check the sender of the email and the domain name of the website to make sure it is the right one. You may not be able to distinguish it from the real website because it will be like a fake clone. Only share your password and other sensitive information after ensuring the credibility of the website.
- Spammers can trick you by sending fake delivery failure messages along with fake links. When someone clicks the link, harmful programs may be downloaded onto their computer. Verify whether it was sent by your email server or not to avoid this. It is spam if it is from a different email address with a different domain.
- Make sure the emails are grammatically correct and don’t contain mistakes like incorrect wording.
- Emails offering free goods and services should be ignored as the chances of a scammer behind it is way up.
- Mark the spam emails you get as spam, this will improve the scam detection ability of your email client software. Later you can check the spam folder and unmark spam for any legitimate emails.
- If your coworker sends you an email and you identify it as spam, then it is because their email account is possibly compromised. You should immediately contact him and ask him to change the passwords before they could be used to send out further spam emails.
7. Clone Phishing
In clone phishing as in conventional phishing, unsuspecting users are compromised via email. As the name implies, clone phishing is a phishing attack that copies an email from a trusted or authoritative source and inserts a link to malware or asks for sensitive information (usually by intercepting a real email before it reaches the intended recipient).
Display name spoofing is done on the senders’ email address which is used to make the receiver believe that it came from their trusted company. The attachment file in the email will be the only file that distinguishes it from the genuine email. To justify why the user was getting the “same” message again, the perpetrator could suggest something along the lines of trying to resend the original or a revised version.
Users are more likely to fall for this attack because it is built on a previously used, genuine message. An attacker who has already compromised one user may use this strategy on someone else who got the cloned email. To deceive the user, the attacker might build a cloned website with a spoofed domain.
Clone phishing emails are sent to large numbers of recipients in the hopes that just one or two recipients will fall for the scam.
How to Prevent Clone Phishing Attacks?
- If the sender’s address looks suspicious, double-check it.
- Verify the source of any included link before clicking it. The URL can be found by hovering over the link.
- Follow up with the organization or individual in a separate email if an email seems suspicious.
- If you need to submit information, always make sure that websites use the HTTPS prefix for the URL.
8. Whaling
Whaling is an attack that is done by the attacker on high-profile employees of a company. This is because they hold much more information about the company rather than any other employee in the company.
The goal of the attacker is to manipulate high-level employees to make a wire transfer to the attacker’s bank account. The word “whaling” refers to the scale of the attacks, and the whales are chosen depending on their company’s authority.
Whaling attacks are more difficult to track and avoid than normal phishing attacks due to their extremely targeted nature.
Countermeasures Against Whaling Phishing Attacks
- Cyber security awareness for employees.
- Multistep verification, i.e all requests for wire transfers and access to confidential or sensitive data should go through several levels of verification before being permitted.
- The servers that hold the data and the emails should undergo malware scans and should also be monitored for security breaches. Proper setup of firewall and scanning programs will be the last hope to prevent attacks on the system.
- Let high-level executives be mindful of social media’s possible involvement in facilitating a whaling breach. Cybercriminals may use social media to craft social engineering attacks like whale phishing because it provides a plethora of knowledge.
Winning the Battle Against Phishing
Phishing is a lucrative business for criminals. To gain profitability, attackers have increased the infrastructure, diversity, and sophistication of their attacks during the last decade in reaction to increased user knowledge and countermeasures.
Hackers are using web browser flaws and obfuscation tactics to build phishing scam pages that are harder to distinguish from legitimate sites, making consumers vulnerable even though they are aware of phishing scams.
But, by understanding more about how a phishing attack is carried out and by knowing the ways to prevent them, you can avoid being a victim of phishing attacks. Thus, it is important to stay up-to-date with all the new phishing scam methodologies and also the countermeasures developed.
